Are there any RFID Privacy Concerns?
Yes, there are Concerns about RFID Privacy!
Unsurprisingly, there are many privacy concerns surrounding RFID technologies. These concerns are particularly so when it comes to personal issues relating to the use of passports, smart cards and the advent of the contactless smart card.
Passports
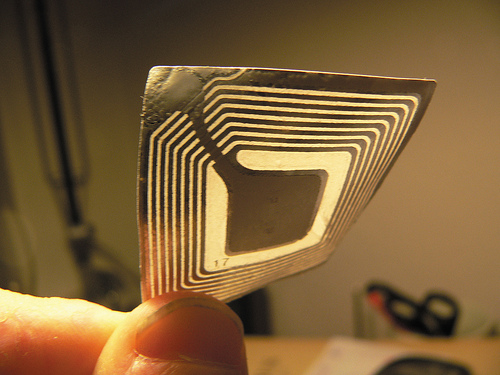
In an effort to make passports more secure, many countries have implemented RFID (biometric microchips) into their passports. However, the encryption on the microchips has been broken. Leaving the biometric passport open to attack from potential criminals intent on stealing your personal information and identity.
There is also the concern that passport data can be scanned while the passport is being mailed to its owner. Where a criminal needed to secretly open and then reseal the envelope, now it can be done without detection, adding some degree of insecurity to the passport system.
Additionally, the RFID passports can be scanned by anyone with an RFID reader from as far away as several hundred feet. This can be a real security risk!
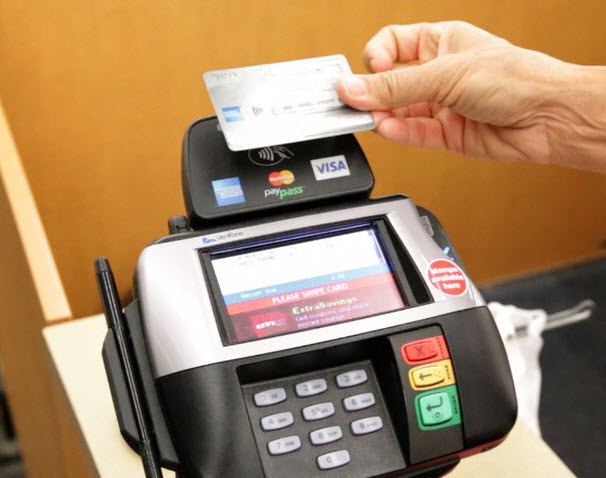
Smart Cards (Credit Cards etc…)
The most popular smart card today is the Credit/Debit Card with an imbedded microchip. Smart cards can provide identification, authentication, data storage and application processing. Smart cards may provide strong security authentication for single sign-on (SSO) within large organizations. These contact smart cards need to be inserted into a card reader to communicate and process transactions.
EMV (Europay MasterCard Visa) compliant cards and equipment are widespread and only since 2014 have been accepted into the United States. MasterCard was the first company that has been allowed to use the technology in the United States. In addition, Chase Bank has also received a contract to use the technology on some of their newer credit card plans.
The United States has felt pushed to use the technology because of the increase in identity theft. The credit card information stolen from Target in late 2013 was one of the largest indicators that its American credit card information was not safe. Target made the decision in April 2014 that they would implement the smart card microchip technology in order to protect themselves from future credit card identity theft.
Contactless Smart Cards
A second type of smart card is the contactless smart card. This type of smart card communicates with and is powered by the reader through RF induction technology (at data rates of 106–848 kbit/s). These cards require only proximity to an antenna to communicate.
Like contact smart cards, contactless cards do not have an internal power source. Instead, they use an inductor to capture some of the incident radio-frequency interrogation signal, rectify it, and use it to power the card’s electronics.
Smart cards have been advertised as suitable for personal identification tasks, because they are engineered to be tamper resistant. The chip usually implements some cryptographic algorithm. There are, however, several methods for recovering some of the algorithm’s internal state.
Thank You
That is the end of our series of articles that we trust have helped you understand what RFID is all about and the possible implications for you when using your credit/debit cards, passport or any other identity cards.
We always recommend that you stay protected at all times. Carry your passport, credit/debit cards and other identity cards in a secure RFID blocking wallet. They provide peace of mind for a very small investment.
Image: PayWave Payments
Continue Reading